
Smart Chiller Plant Optimization at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Project Overview
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU), located in Hung Hom, Kowloon, spans 80,000 square meters. The university's largest chiller plant, which provides cooling to approximately 50% of the campus, including key buildings such as academic offices, libraries, and dining halls, was experiencing significant inefficiencies due to its reliance on an outdated, manual control system. The chiller plant consumed around 9 million kWh of electricity annually, leading to operational costs of 11 million HKD. To address these challenges and enhance operational performance, our team implemented an advanced AI-driven smart building energy management system, optimizing energy usage and improving overall efficiency.
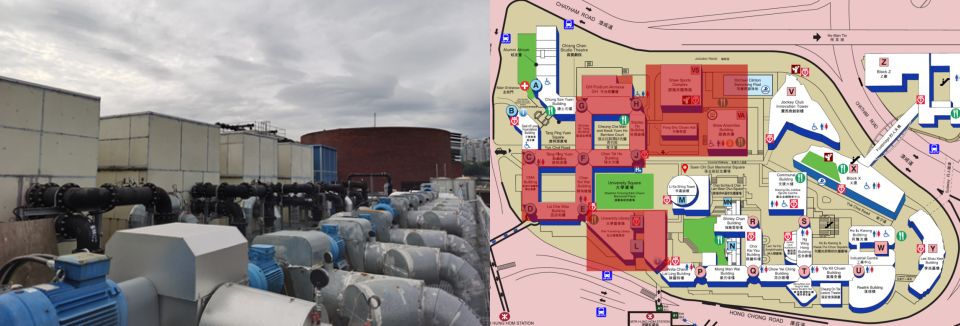
Project Highlights
Advanced Technologies and AI Models
The project employed our proprietary Smart Building Energy Management Platform, deployed on the Windows platform, to optimize the operation of existing chiller plant. This advanced platform integrates our proprietary AI algorithms and models, enabling real-time performance monitoring and optimal control of the plant. Key technologies implemented include:
•AI-Driven Chiller Sequencing Optimization.
•Data-Driven Predictive Chiller Plant Health Monitoring.
•Physics-Guided Pump Sequencing Optimization.
Energy Efficiency and Savings
The AI-driven optimization system achieved consistent monthly energy savings of 22.2%, daily cost reductions of 7,353 HKD, and projected annual savings of 2.5 million HKD, with potential campus-wide savings of up to 8.6 million HKD.
Platform Visualization and User Interface
The self-developed Windows-based visualization platform enables real-time monitoring, intuitive dashboards, and proactive maintenance alerts, enhancing transparency and accessibility in energy management.

Acknowledgments
This innovative project was supported by leading research initiatives, including the 2020 National Key R&D Program of China's Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) and the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Fund (ITF), highlighting its importance in advancing smart energy management solutions for complex building systems in high-density urban environments.